Token The term non-fungible token (NFT) generally refers to a cryptographic asset on the blockchain that represents a unique, intangible digital item such as a piece of art, a photo, or a game. collectible, or a tweet that other assets can’t replace because it has a set of exceptional properties. Each NFT is unique and limited in quantity and non-tradeable; it can function as proof of authenticity and ownership.
NFTs are distinguished from one another by metadata and unique identifiers such as a barcode. The information that makes up the asset is known as metadata. Metadata allows users to buy or sell items based on their metadata rather than the entire item.
NFTs aim to replicate tangible attributes of physical items such as uniqueness, scarcity, and proof of ownership. On the other hand, expendable goods may be interchangeable because their value, not their unique characteristics, characterizes them. However, digital products are only valid when used in conjunction with your product.
NFT prototypes were colored coins, referring to experimental assets created on the Bitcoin network in 2012. The first asset representing a non-fungible tradable blockchain marker was created in 2014 as an experiment for the Seven on Seven conferences. at the New Museum in New York. City.
While digital collectibles and art NFTs continue to attract the most attention in the crypto community, their potential use cases continue to rise. They expand from general use cases like digital art and games to fashion, music, academia, tokenization of real-world objects, patents, membership sales, and loyalty programs. There is also room to combine the advantages of NFT technology with the functionality of decentralized finance (Defi). For example, non-fungible tokens can be borrowed and lent and can be used as collateral to secure a loan.
Anyone interested in selling and sharing their digital creations such as content, art, music, and photography can create NFTs. Here is a practical guide to successfully jumping on the non-fungible token creation bandwagon.
The creation of NFTs is a fairly simple process. For example, users can choose their content and get a crypto wallet. They can choose a suitable NFT market and follow its instructions. Once an NFT is created, it is ready to be sent to friends or sold to collectors.
This is what you need to know more about the NFT creation process.
Read more: The NFT Market: How to Buy and Sell
Understanding
NFTs An NFT collector paid $69.3 million for digital artwork titled “Every day’s: The First 5000 Days” by Mike Winkelmann aka Beeple, making this the most expensive NFT in the history of crypto art. The CryptoPunks Collection consists of 10,000 pixelated images of punks with a unique feature set, pioneered in 2015 on the Ethereum blockchain, selling for thousands of dollars.
The question arises: What is the value of these digital creations and why do collectors spend so much money on them?
Beeple’s “Every day,” a collage of 5,000 drawings referencing every day for the past thirteen and a half years, was an arduous task. However, many NFT collections, which are incredibly successful, probably don’t require a particularly complex contribution from the author.
Therefore, for anyone who wants to become an NFT artist, having a goal in mind and a high level of creativity is a must. Even for those who are not as skilled as Leonardo da Vinci but have a ton of ideas, creating an NFT is certainly worth a try. Also, for artists by occupation who likely already have several Beeple-like artworks sitting idle in the digital studio and waiting in the wings to be sold as NFTs, this could be a great starting point.
Truth be told, an unknown person’s innovative and engaging digital artwork won’t rise to the level of insane like celebrity creations like Canadian singer Grimes’ 10 digital paintings that have sold for around $6 million, NFT releases. from Kings of Leon that have generated $2 million in sales, or an exciting NFT featuring Jack Dorsey’s first tweet, which sold for over $3 million.
After all, NFT technology is ideal for preserving scarcity and establishing ownership of digital and tangible assets. It offers digital creators robust options for monetizing their work and a level of flexibility often lacking in traditional creative industry models. Attaching digital content to the blockchain as a non-fungible token is a secure and verifiable way to sell it online. Furthermore, the creation of NFT gives artists unlimited access to a global network of collectors and like-minded people.
Fortunately, the process of creating an NFT is not expensive, complex, or technical. Without writing any code and with the proper guidance, anyone can create an NFT.
Choose the format and choose your content
First of all, creators need to choose the format of their NFT. They can generate a non-fungible token from any media file. It can be a digital painting, a photo, a text, an audio file, or a video of some notable event. There are other creative products like crypto-collectibles, virtual video game items like avatars, weapons, and currency, as well as virtual lands in metaverses that can also be represented as NFTs.
Of course, there’s room for creator ideas here, as it seems like everything digital could be an NFT these days. For example, it could be the source code for the World Wide Web, which was sold by its inventor, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, in the form of NFTs for $5.4 million, a “high-resolution artistic rendering” of the data genetic studies of Professor George Church, or the data of the first person to sequence their own DNA. Additionally, there is still a place for non-digital tokenized real-world assets, from real estate and diamonds to designer sneakers, all of which are sold in the form of NFTs.
When it comes to formatting, creators have complete freedom of choice. It may depend on the theme of your artwork and your imagination.
Please note that after creators decide what content and in what format they want to represent as NFT, they will need to convert it to an appropriate file type, especially if it is not yet digital. Most items tend to be stored as Portable Network Graphics (PNG) or Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) files. Texts would normally be available in Portable Document Format (PDF), while music would likely be stored as MP3 and video saved as MP4.
How to create and mint NFTs
The value of NFTs is defined by their uniqueness. There are situations where users may want to create multiple identical copies of their creations. For example, if you are selling a collectible, you could offer different versions, some more exclusive than others. In this case, you need to decide how many identical copies of a particular NFT to include within the blockchain because this number will be fixed and your NFTs will become immune to any modification after their creation.
The process of creating a non-fungible token is called minting. The term refers to the process of turning a digital item into an asset on the blockchain. Similar to how metal coins are created and put into circulation, NFTs are minted once they are created. After the process, the digital item becomes tamper-proof, more secure, and difficult to tamper with. Since it is represented as a non-fungible token, it can then be bought and traded, as well as digitally tracked when it is resold or collected again in the future.
Some NFT technologies allow ongoing fees to be paid to the original creator each time a referenced item changes ownership. By minting a token, creators can program a royalty clause so that subsequent sales of their digital items will generate passive income for them. If their work becomes popular and increases in value, they can make a monetary profit.
The minting process begins when you sign your NFT and pay the gas fee. You will be able to see your newly minted NFT in your profile after the transaction has been validated.
Choose the NFT market
After the digital item for a future NFT is ready, it is time to choose an NFT market to sell it.
Choosing a platform is an essential part of the NFT minting process, and the right choice here depends on several factors, including certain types of blockchains, supported formats and standards, accessibility, and a price to mint an NFT.
The first standard to represent non-fungible digital assets on the Ethereum blockchain was ERC-721. The ERC-1155 standard offers semi-fungibility. Unlike ERC-721, where the unique identifier represents an asset, the ERC-1155 token’s unique identifier represents an entire class of fungible assets, any number of which the user can transfer to others. Components based on the ERC-998 standard are the templates according to which NFTs can be non-fungible or fungible assets.
Ethereum does not have a monopoly on NFTs. However, most of the platforms are based on Ethereum. Other non-Ethereum NFT markets belong to blockchain ecosystems like Cosmos, Polkadot, or Binance Smart Chain, to name a few.
Read more: 10 best nft marketplace in year
Each of the NFT markets works slightly differently and has its specific instructions as well as its advantages and disadvantages. For example, some of the NFTs are selective, while others are self-service based. Creating NFTs on some platforms is cheaper than on others, while some markets don’t support specific file formats. Some platforms are easy to use, while others have a complex user interface (UI) that might be intimidating for new users.
Currently, there are many NFT markets in the crypto space. Unselected platforms have emerged as a viable alternative to selected ones as they provide free access to all. To load NFTs on them, users just need to register and pay the transaction fee to mint a token.
An unselected platform is OpenSea, which allows users to mint and trade NFTs, view data about them, and view statistics. Created in 2017, OpenSea keeps almost all the collections of crypto art, as well as a large number of items from many popular blockchain games. The platform has a fairly easy-to-use creation interface that allows users to quickly and efficiently create a non-fungible token for free.
Another massive market is Rarible, a self-service platform that is interconnected with OpenSea. The process of creating an NFT in Rarible is very similar to that in OpenSea, but its functionality is slightly different. For example, the number of formats is limited and the size of artworks is smaller. However, Rarible has high traffic and allows users to mint tokens before they are sold, while OpenSea handles the minting of tokens when they are sold.
Unlike the self-service platforms, the selected ones are more selective with the creators. To start selling digital content on SuperRare or Nifty Gateway, creators must submit an application form with strict selection criteria and a long waiting period for the experts’ decision.
Set up a wallet and own some cryptocurrency
A cryptocurrency wallet is a critical component of any blockchain system. According to the basic principles of blockchain, users need wallets to access different platforms, sign transactions and manage their balances. Therefore, NFT markets eliminate the need to store user account data, making the platform more secure.
Various cryptocurrency wallet apps are available on smartphones to buy and store cryptocurrencies. Many are designed specifically for newcomers to blockchain and can guide them through transaction fees, security, and privacy.
There are many crypto wallets and browser extensions to access blockchain-based applications that can get the job done. Some offer greater security beyond a simple email address and password with an initial twelve-word passphrase. Before setting up a wallet, the most important thing is to make sure that it matches the cryptocurrency used on the platform you intend to use.
When looking to mint a token on the blockchain, users must pay a gas fee. A gas fee refers to a payment made by the user to offset the computing power required to process and validate transactions on the blockchain. A gas limit is the maximum amount of gas a user is willing to spend on a particular transaction.
Gas rates fluctuate significantly depending on the level of demand to create transactions. Minting an NFT can be free. However, it could cost between $10 and $100, depending on the chosen market. Gas fares are significantly cheaper (on average) on weekends when fewer people are transacting, which will help NFT enthusiasts keep costs down if they mint multiple items.
Multi-item minting differs from double minting, which refers to minting the same NFT twice. Users are not restricted from taking the same digital item already minted in one NFT market to a different one, minting it a second time, and selling it again as a new NFT. Users should be aware of all potential reputational consequences, such as the depreciation of the specified NFT and any subsequent digital items the user wants to sell, as the user’s credibility could be undermined. Therefore, double minting should be prevented by inserting an invisible code into the file of a digital item without significantly affecting the appearance of the item to the naked eye.
Users can then download the cryptocurrency wallet app on both their smartphones and personal computers to access NFT sales receipts, as they will need to have a way to receive cryptocurrency and convert it to traditional money whenever they want.
There are two main ways to convert crypto into cash and eventually transfer it to a bank account. First, you can use third parties like crypto exchanges, ATMs, and debit cards. The second option is to use a peer-to-peer (P2P) platform. Both methods are simple and safe. However, using a peer-to-peer transaction tends to be a faster and more anonymous way to exchange your crypto for cash at a predetermined rate.
Follow NFT Platform Instructions
Each NFT marketplace has specific instructions that creators will need to follow to create a non-fungible token.
First of all, the market usually asks users to upload a file they want to convert into an NFT with a title and a short description. Ideally, NFT platform users should spend some time filling in the details of their non-fungible tokens and perfecting them to attract collectors and maximize the chances of selling their creations. After uploading the digital item, they will also need to choose whether to mint a single token or a collection.
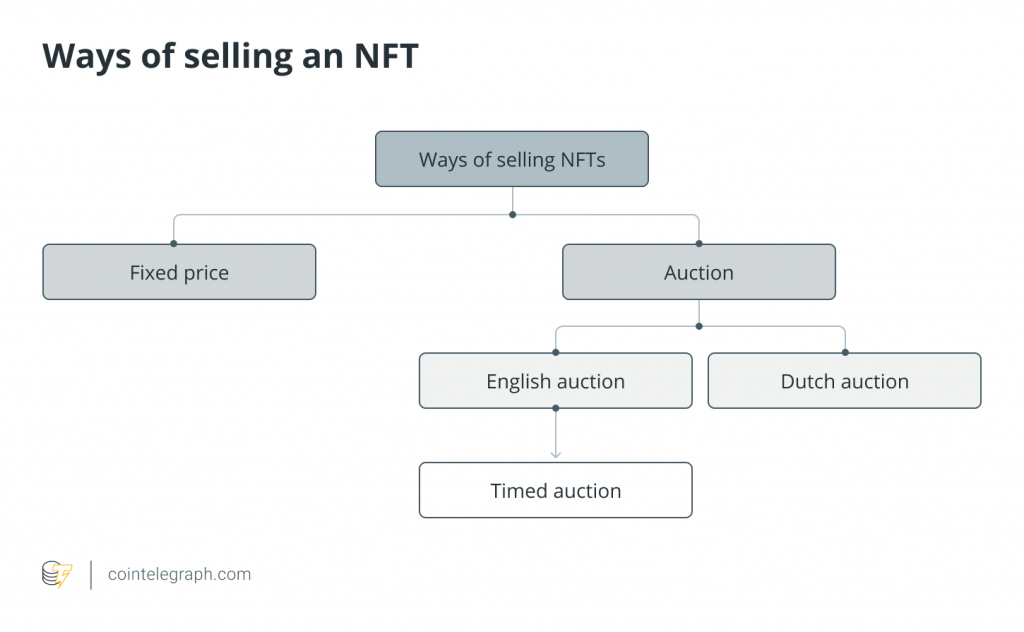
Second, there are two possible options for selling NFTs: fixed price or auction. A fixed price sale is where users specify a price at which they want to sell the NFT. It is quite transparent and direct. Auctions are another exciting way to sell NFT creations. There are generally two types of auctions available on different NFT markets. The first type is an English auction, which is an auction of increasing price and the highest bid wins at the end. There is also a form of English auction called a timed auction where each lot can be bid for a defined period and at the end of the period, the collector who has submitted the highest bid wins and buys an NFT. The second type is a Dutch auction, also known as a falling price auction, where the price drops until someone buys an NFT.
Then, depending on the market chosen by users, they will need to set an initial price for their NFT. Some marketplaces also ask to set a royalty percentage, which is the amount that users will receive when future collectors sell their NFT. Setting a percentage is a balancing act, as a higher percentage will make you more money per sale, but it will also deter people from reselling your art in the first place, as they will be less likely to make a profit for themselves.
Additionally, there will be an option to add file properties such as optimal resolution and size. Finally, the platform verifies the token and if approved, it is ready for sale.
NFT Promotion
With all said and done, users can choose to actively promote their newly minted NFT creation. The promotion of an NFT will depend on the details of the user’s NFT. However, there are some basics that creators can pay attention to, such as understanding the buyer or creating an effective promotion strategy.
One of the most efficient promotional techniques is public relations, which refers to developing a positive reputation within the community by sharing favorable information about you and your NFT collection.
In addition, it could be promoted through online advertising, including publications in specialized newspapers and appearances in crypto podcasts, as well as promotion on social networks.
If the creators are looking for the biggest collectors, it would make sense to attract the largest possible audience, and the use of social networks could be very useful since users can share the links to their digital items on their social networks and on the NFT market. Twitter, Telegram, and Discord have already established communication channels for the crypto community, where users can create personal accounts on them to promote their NFTs, establish a reputation, and improve general awareness. Consequently, they may meet some influencers and artists to collaborate with or popular media journalists who are willing to write about themselves and their NFT collection.
For NFT creators, developing a loyal community could be vital for promotion, as these people will constantly support them, spread the word about them, invest in them, and willingly buy their NFT creations.